Application Challenges
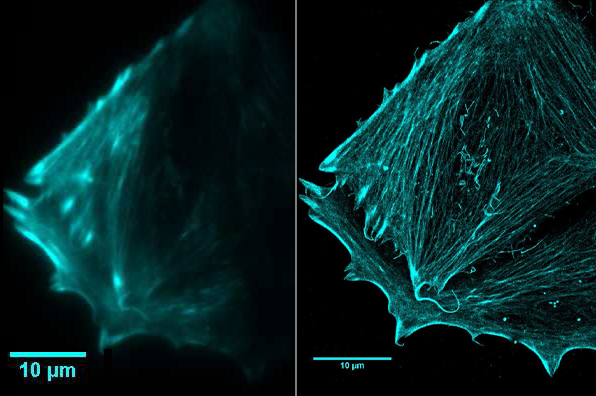
Super-resolution techniques, such as STED, SIM, and PALM/STORM, surpass the diffraction limit of light, enabling researchers to resolve cellular structures and molecular distributions with nanometer-scale precision.
While these methods achieve unprecedented spatial resolution, they come at the cost of photon efficiency. Many techniques require acquisition of thousands of sequential frames—for example, single-molecule localization methods (PALM/STORM) reconstruct one high-resolution image from tens of thousands of localizations. Additionally, concentrating light into extremely small regions increases local energy density, heightening the risks of photobleaching and phototoxicity. These challenges impose stringent requirements on camera systems, demanding ultra-high sensitivity, exceptionally low noise, and high-speed imaging capabilities.
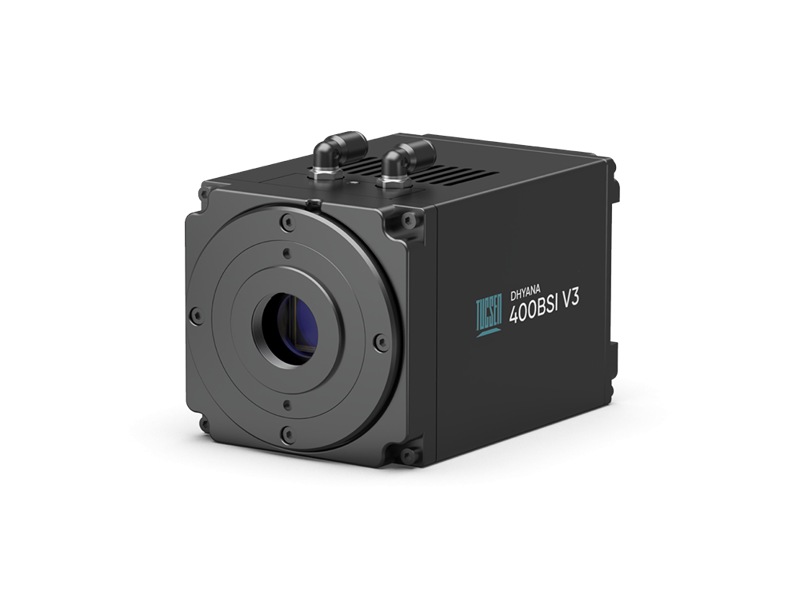

Dhyana 400BSI V3
Classic 6.5 µm BSI sCMOS Camera
Pixel Size: 6.5 µm, optimized for 40×–60× high-NA objectives.
Shutter Modes: Multiple rolling shutter modes, tailored for scanning and light-sheet imaging.
Calibration: PRNU/DSNU correction ensures uniform background for accurate quantitative analysis.
Interface: USB 3.0 and Camera Link.
Cooling: Water + air cooling design for stable, low-noise operation.
Compact Design: Lightweight at 995 g, low power consumption of 45 W.
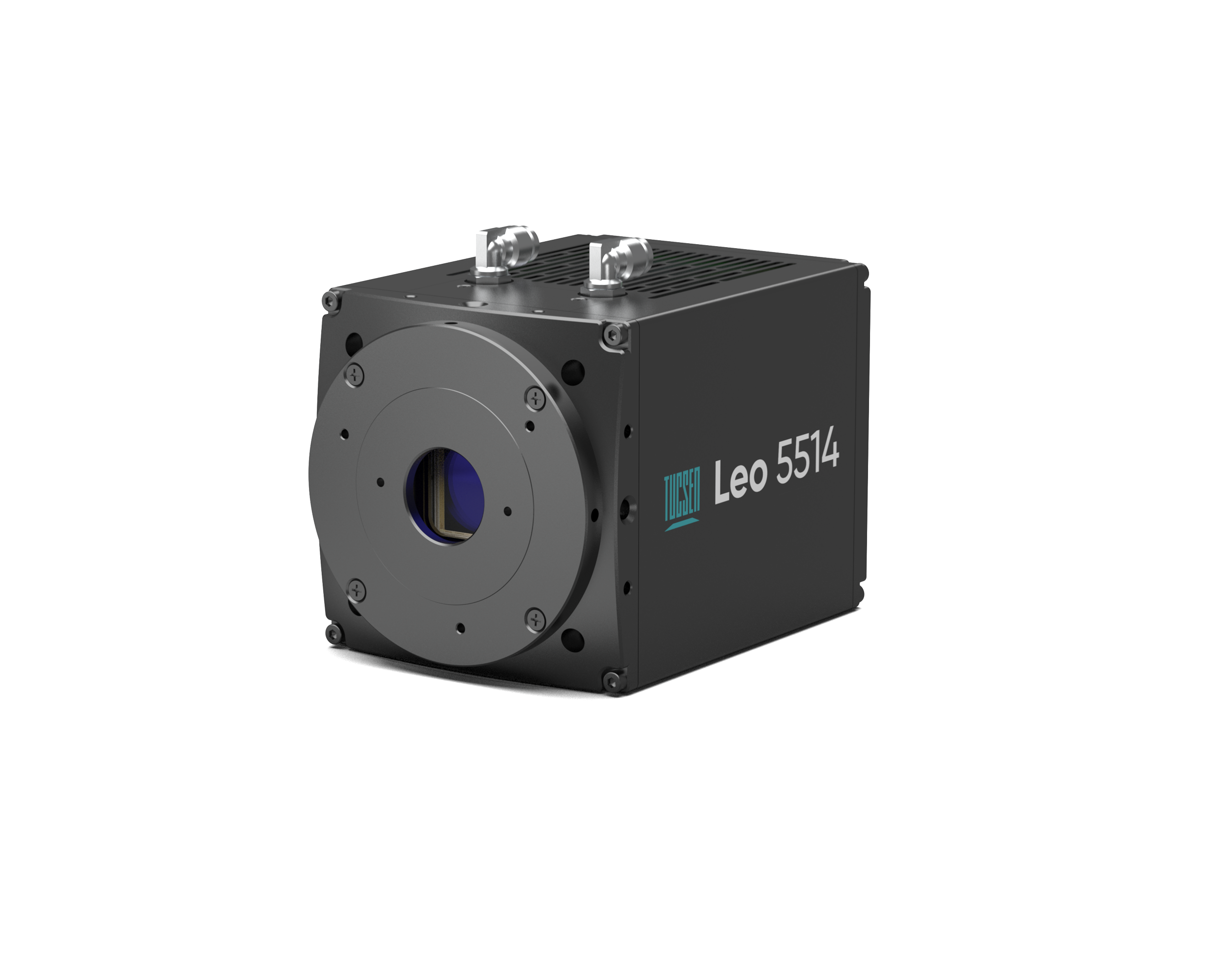

Dhyana 95 V2
Classic 11 µm BSI sCMOS Camera
Pixel Size: 11 µm, ideal for Nyquist sampling with 60×–100× high-NA objectives.
Sensor Area: Large 32 mm imaging area for extended field-of-view imaging.
Full-Well Capacity: High, supporting quantitative measurements with a wide dynamic range.
Interface: Dual options – USB 3.0 and Camera Link.
Cooling: Hybrid water + air cooling system effectively suppresses dark current.
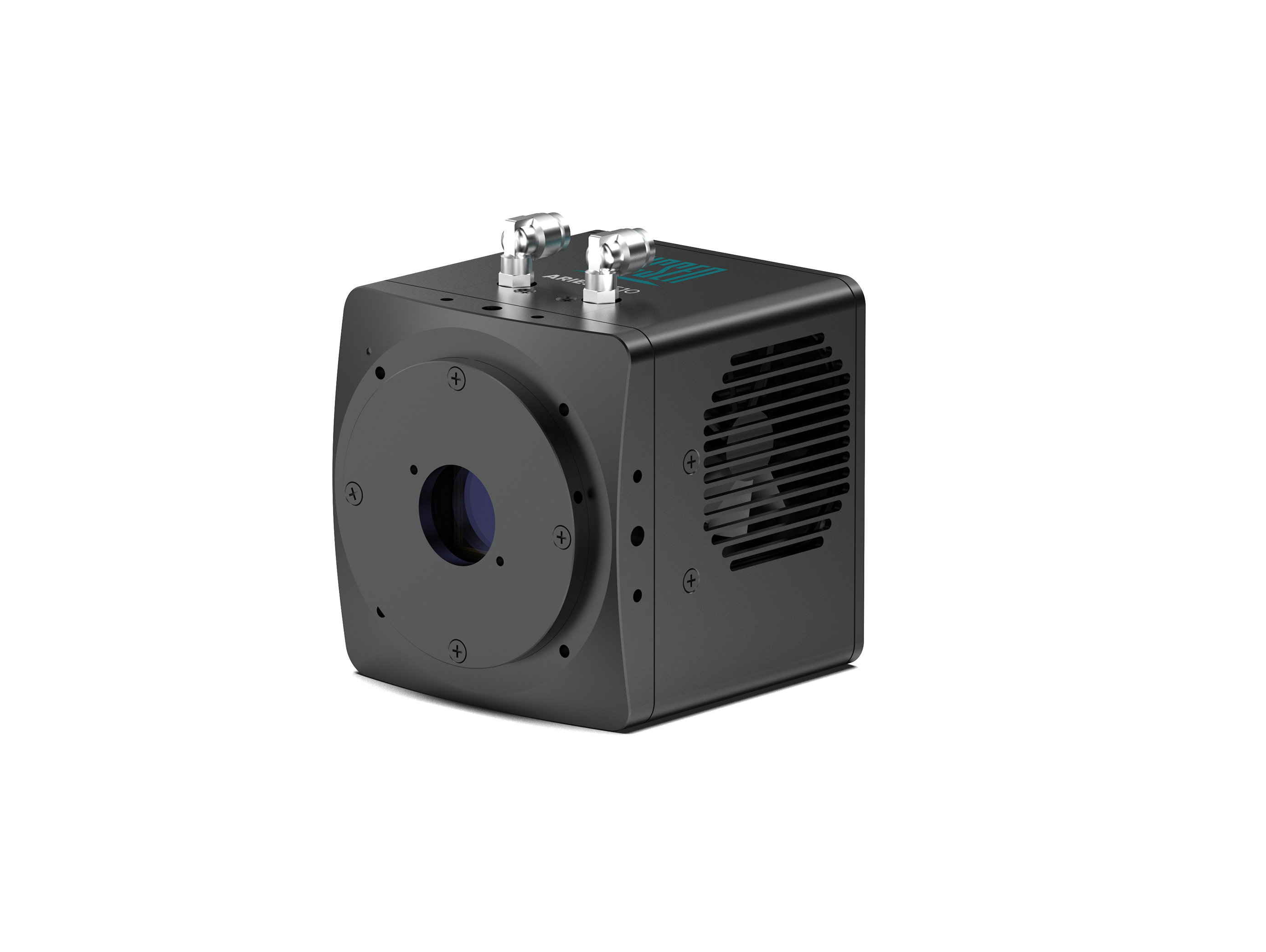

Aries 6510
Large-Format 6.5 µm BSI sCMOS Camera
Quantum Efficiency: Peak QE up to 95%, near single-photon detection capability (<0.7 e⁻ readout noise)
Sensor Area & Resolution: 29.4 mm imaging area, 10.2 MP resolution, full-frame readout up to 150 fps.
Pixel Size: 6.5 µm, versatile across multiple magnifications.
Readout Modes: Multiple readout modes for optimized performance.
Interface: High-speed GigE interface.
Cooling: Forced-air cooling minimizes noise drift and ensures stable quantitative imaging.